PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
201-337-8
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white to off-white crystalline powder
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
- Cholic Acid
- Methyl Cholate
- Deoxycholic Acid
- Dehydrocholic Acid
- Methyl Deoxycholate
- Chenodeoxycholic Acid
- Methyl Chenodeoxycholate
- Sodium Glycocholate
- Glycodeoxycholic Acid
- Sodium Glycodeoxycholate
- Sodium Taurocholate
- Sodium Taurodeoxycholate
- Ursodeoxycholic acid
Commecial bile acids' application fields include:
- Experimental basis of cathartics, cholagogues
- Preventing and dissolving gallstones.
- As an intermediate for the production of corticosteroid structure drugs to treat various disorders such as pain or inflammation, brain tumors, skin diseases, and allergic reactions.
- As detergents to emulsify biological fats.
- Vaccine delivery system
EXAMPLES
OF NATURALLY OCCURRING CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
(excluding
fatty acids)
|
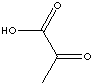
Pyruvic acid |
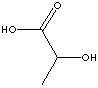
Lactic Acid |
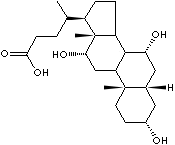
Cholic acid |
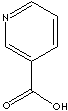
Nicotinic acid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
metabolic intermediate |
metabolic intermediate |
from bile |
vitamin B |
|
|
|||
|
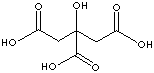
Citric acid |
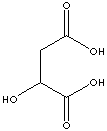
Malic Acid |
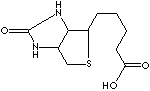
Biotin |
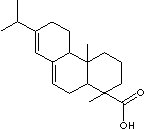
Abietic acid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
in plants |
in fruits |
cell growth factor |
pine rosin |
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0% min